Geolocation technologies have been booming for several years, and are not about to disappear.
Indeed, with the exponential growth of products and equipment in circulation around the world, geolocation has become a major challenge for in most companies.
Today, many geolocation solutions are being developed, and it can be difficult to find your way around and, above all, to choose the one that best suits your needs.
So how do you make the right choice?
In the following article, we will explore the various geolocation technologies that exist; how they work and the advantages and constraints of each technology.

What is geolocation?
First of all, let’s take a look at / delve into what is meant by geolocation in a more general sense.
Have you ever wanted to know where your delivery is in real-time, or to locate interesting places nearby?
If so you have probably already used geolocation technology.
Geolocation is the process of determining the geographical position of an object or a person using various technologies such as GPS, cellular network, Bluetooth Low Energy etc…
But
Let’s not get ahead of ourselves, we’ll come back to the wide range of solutions in more depth later in the article.
Geolocation: Indoor vs Outdoor
Is the item you want to track intended to be used indoors or outdoors?
Depending on the location of the asset to be tracked, there are two main categories of geolocation: outdoor geolocation (outdoors) and indoor geolocation (indoors).
Outdoor geolocation allows the geographic position of an object or person to be determined in the open air.
Indoor geolocation is used inside a building.
Whether we are talking about outdoor or indoor geolocation, the challenges are the same: to provide permanent visibility and to optimise and secure the company’s activities in order to ensure maximum profitability.
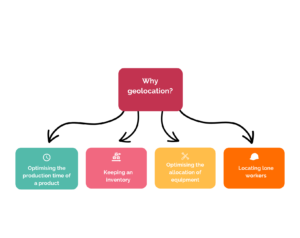
Depending on the needs, geolocation technologies can meet many objectives, for example:
Optimising the time it takes to manufacture a product by tracking it through all the stages or by triggering alerts in the event of delays.
Maintain an automatic inventory of industrial equipment and stock to obtain a global view.
- Optimise equipment allocation by sending the closest equipment to where it is needed or by alerting to use outside the authorised area (e.g. theft).
- Locate lone workers in case of emergency and allow emergency services to intervene quickly thanks to an alert system.
The key to finding your most suitable technical solution is to precisely identify your objectives, at the start of the project.
The basic principles of object geolocation
A geolocation technology consists of transmitters and receivers.
They are closely linked, as one uses the position of the other to determine its own position.
The number of transmitters and receivers and the way they work can vary from case to case.
Here are a few examples to guide you, depending on your geolocation needs and objectives:
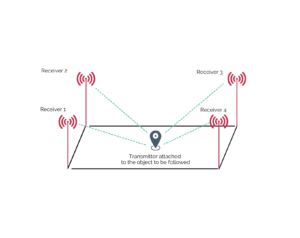
Case 1: Multi-receivers
In this case, there is one transmitter and several receivers.
To locate the object, a transmitter is placed on it, while known-position receivers listen to the transmitted signal.
The Received Signal’s attributes, such as Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), Time Of Flight (ToF), Angle Of Arrival (AoA), etc., are then collected and sent to a calculation unit, which processes this information to determine the transmitter’s position.
For example, a multi-receiver solution can be used for object location in an industrial shed with BLE or Ultra-wideband (UWB) technology.
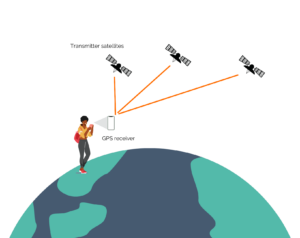
Case 2: Multiple transmitters
Here, it is the turn of the transmitters, whose position is known, to send a signal.
The receiver is attached to the object whose location we wish to track and listens to the signals sent by the transmitters.
If the receiver knows the position of the transmitters and has the appropriate computing power, it can determine its own position from the signals received.
If not, the receiver can send the collected signals to a computing unit which then determines the position of the transmitter.
The multi-transmitter system allows, for example, the location of an object with GPS.
The different geolocation technologies on offer
There is a wide range of geolocation solutions available today.
Before launching yourself, it is essential to study them in order to choose the one that will be the most adapted to your needs.
Here are the most commonly used technologies today and their characteristics:
GPS
We all know it and have used it, but do you really know how GPS works?
In general, when we talk about geolocation, we often think of GPS.
GPS is, in fact, historically one of the first geolocation systems and the most widely used today.
It is mainly used for outdoor geolocation, as it cannot meet the needs of indoor positioning.
Positioning via GPS offers an accuracy of between 5 and 50 metres.
The disadvantage? It requires quite a lot of energy (compared to alternatives such as WIFI and LoRaWAN, which are admittedly less accurate).
This makes it incompatible with certain products that run on batteries and that need to last for several years, for example.
How does the GPS work?
Let’s go into a little more technical detail…
GPS receivers “listen” to the signals emitted by a set of satellites that circulate around the earth.
By knowing the positions of the satellites and the time the satellites sent the message, the GPS receiver can determine its own position.
However, as you may have guessed, GPS has its limits: energy consumption and indoor geolocation.
It has therefore been necessary to develop other geolocation technologies that consume less energy.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Unlike GPS, which uses satellites to determine position, BLE geolocation is based on communication between Bluetooth devices.
Often for indoor use, BLE has many advantages due to its low energy consumption and low price.
BLE is the Olympic champion of low energy consumption.
Indeed, it allows the product to run on button batteries for several months or even years.
However, BLE also has its limitations: its sensitivity.
BLE signals are very sensitive to obstacles and metal objects where the signal can bounce and change direction.
Depending on the mesh size of the site, the accuracy is between 2 and 20 metres. Indeed, the more anchors are present on the walls of the site, the more accurate the location will be.
How does BLE work?
If you opt for this geolocation solution, here is how it works:
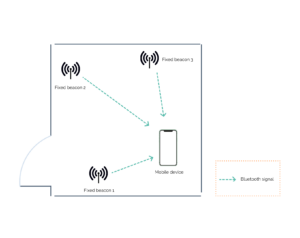
A BLE receiver is attached to the object whose position you want to know.
The transmitters, which are called Beacons, are attached to the wall and constantly emit a signal.
The receiver uses the characteristics of the received signals and the positions of the Beacons to determine its own position.
This is a case of multiple transmitters, but it would be possible to reverse the system to a multiple-receiver system (receivers on the wall and transmitters on the object).
Bluetooth Low Energy is also used to zone manage entries and exits. In this case, the objective is not to have the position of the object but to know if it is in a zone or not.
In this case, a transmitter and a receiver will suffice.
If the receiver obtains the signal from the transmitter, it means that it is in the area it covers.
It is used, for example, in some museums to adapt a message to the visitor depending on where he is.
Ultra Wide Band (UWB)
Because there is a solution for every problem… This technology is often used on the market to overcome the drawbacks of BLE technology.
Unlike Bluetooth Low Energy, Ultra Wide Band is very insensitive to obstacles and bounces.
It allows a precision between 10 cm and 1m.
However, UWB Beacon or Anchors have a higher power consumption compared to BLE (2 to 3 times higher).
How does Ultra Wide Band work?
In the context of geolocation, its operation is similar to the Bluetooth Low Energy solution.
The object is fitted with a transmitter, while the walls of the site are installed with receivers.
Conversely, if the transmitters are stationary, the object can have a receiver installed on it.
The accuracy of geolocation is the primary differentiating factor between these two methods.
The wifi network
Omnipresent in our daily lives, the wifi network is also a powerful geolocation solution.
Extremely well-developed today, it is a good alternative to GPS, particularly in urban areas, as it requires less energy.
This geolocation system uses the known position of certain Wifi networks to determine the position of a device.
The accuracy offered by this solution is between 10 and 50m.
How does the Wifi network work?
Indeed, companies like Google or Mozilla have a database of more than a billion wifi access points with their geographical positions.
Thanks to the Google cars that drive around the cities, taking photos that can be used for Google Street View for example, the wifi networks are identified and listed in the database.
These companies expose an API, which by receiving a list of wifi access points, returns the position where we are.
This technology, which consumes little (3 to 5 times less than GPS), allows for good precision, particularly in urban areas.
It should be noted, however, that, unlike GPS, with this solution, the product needs to send the access points collected to a cloud so that its position can be determined.
The cellular network
The cellular network is not just about connecting you to the Internet via your phone.
Geolocation via cellular networks works in the same way as geolocation via WiFi access points.
In this case, the relay antennas normally used for mobile phone data transfer are used.
The accuracy varies according to the number of base stations. For example, in the city, the accuracy is between 250m and 1km, while in the countryside it varies between 1 and 2 km.
How does the cellular network work?
Just like wifi networks, companies such as Google or Mozilla have a database of more than a million cellular antennas.
These databases know the position of these antennas.
By scanning the surrounding antennas, we can use the Google or Mozilla API to find our position.
The LoRaWAN
Last but not least… The Low Power Wide Area Networking (LoRaWAN) is a cost-effective and efficient geolocation solution.
It relies on the Long Range (LoRa) antennas of an existing public network.
This technology has several advantages: it is easy to deploy and does not require any infrastructure, and offers an accuracy ranging from 250m to 2km.
Moreover, it consumes little energy (as you will have understood, energy is the sinews of war).
How does the LoRaWAN work?
In a public LoRaWAN network, a message sent by one transmitter can be received by several relay antennas.
As the received message is sent back to the LoRa server, the antennas also report the strength and time of reception of the signal.
Using this data on the server side, the position of the transmitter can be deduced by trilateration.
Unlike geolocation solutions based on wifi or cellular networks, this time there is no need to scan. You simply have to send a short message over the network.
5 key questions to ask yourself when choosing a geolocation solution
When looking for a geolocation-based solution, it is important to take the time to ask the right questions in order to make the best possible choice.
The wrong choice can be costly in terms of time, money and performance.
These questions will allow you to narrow down the list of possibilities and identify the most suitable one:
- In what environment do you need geolocation? Outdoor? Indoors? Or both?
This is an essential question, as it will initially enable you to eliminate several technologies out of hand. Indeed, some geolocation solutions are not compatible with one type of environment (indoor or outdoor for example).
- What is the desired accuracy?
Accuracy varies according to the equipment. Some technologies allow a high level of accuracy; to the nearest metre or even less.
Ultra Wideband technology allows this and can be used when the situation requires precise location.
A cellular network, on the other hand, often gives an accuracy of more than one kilometre.
- What is the desired frequency of localisation (punctual, real-time or event-driven)? What is the expected lifetime? With which power source?
By answering these questions, you will be able to determine the energy budget available for geolocation.
This will enable you to rule out certain energy-intensive technologies, particularly if your product is battery-powered and must live for several years without its battery being changed.
- Is it possible to install an infrastructure in the place where your object is due to be located?
Indeed, several indoor localisation solutions require the installation of an infrastructure in order to be operational.
For example, geolocation solutions such as Bluetooth or Ultra-Wideband require an infrastructure to be installed on-site.
- Does the object to be geolocated already have a means of communication?
Communication protocols such as Long Term Evolution, LoRa or Sigfox, make it possible to locate equipment sending a message.
So if your object already has access to such a resource, there may be a way to use it for geolocation depending on your coverage and accuracy criteria.
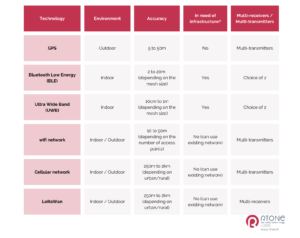
To refine your search and find the technology best suited to your needs, you need to take the time to properly identify them and define your objectives.
It is important to take into account the environment in which the geolocation solution will be integrated, as well as the required accuracy, power consumption and cost.
Indeed, a geolocation solution can have a very high performance and accuracy. However, if it consumes a lot of energy or costs a lot of money, it may not be the most suitable for your needs.
At Rtone, we have already assisted our clients in this kind of way through audits and personalised comparisons.
Please contact us to find out more about our services.